TianYi Lu1, Hao Cheng1, Yoshio Takahashi2, Tsuyoshi Iizuka2, Qiong Chen1, and Limin Gao1
1 State Key Laboratory of Marine Geology, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
2 Department of Earth and Planetary Science, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
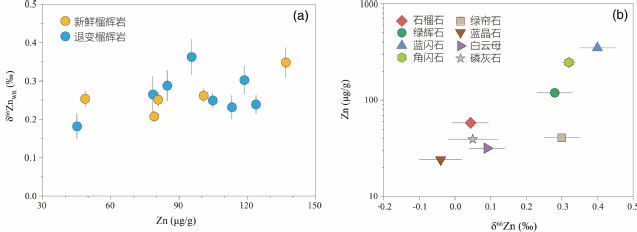
Abstract: High-pressure eclogites with continental affinities exposed on Earth’s surface offer insights into the subduction process. However, the isotopic characteristics of zinc in these subducted continental crustal materials are rarely explored. In this study, we report Zn isotope compositions of minerals and whole rocks for fresh and retrograded continental eclogites from the Dabie orogenic belt. Fresh eclogites display δ66Zn values ranging from 0.21‰ ± 0.01‰ to 0.35‰ ± 0.04‰, whereas retrograde eclogites exhibit a broader range from 0.18‰ ± 0.03‰ to 0.36‰ ± 0.05‰, both higher than typical mantle values (0.16‰-0.20‰). The absence of correlations between δ66Zn values and major oxide contents (Al2O3, MgO, FeO, and TiO2) or fluid-mobile indicators (Ba/La, Pb/Ce, Nb/U, Rb/TiO2), along with the linear correlations between TiO2 and other oxides as well as high field strength elements (Nb, Y, and Hf), suggests that Zn isotopes do not reflect magmatic processes and are largely unaffected by metamorphic fluid-rock interactions. This implies that Zn isotopic variations in continental eclogites likely reflect the inherent heterogeneity of their protoliths. Significant inter-mineral Zn isotope fractionation is observed in both fresh (-0.09‰ to +0.38‰) and retrograde eclogites (-0.04‰ to +0.40‰). Mass balance reconstructed whole-rock δ66Zn values are consistent with the measured bulk values, probably suggesting equilibrium fractionation amongst minerals during the subduction-exhumation cycle. This is further supported by the consistent Δ66ZnOmp-Grt values in both fresh (0.25‰ ± 0.07‰) and retrograde (0.27‰ ± 0.08‰) eclogites.
Full article:https://doi.org/10.1130/B37987.1